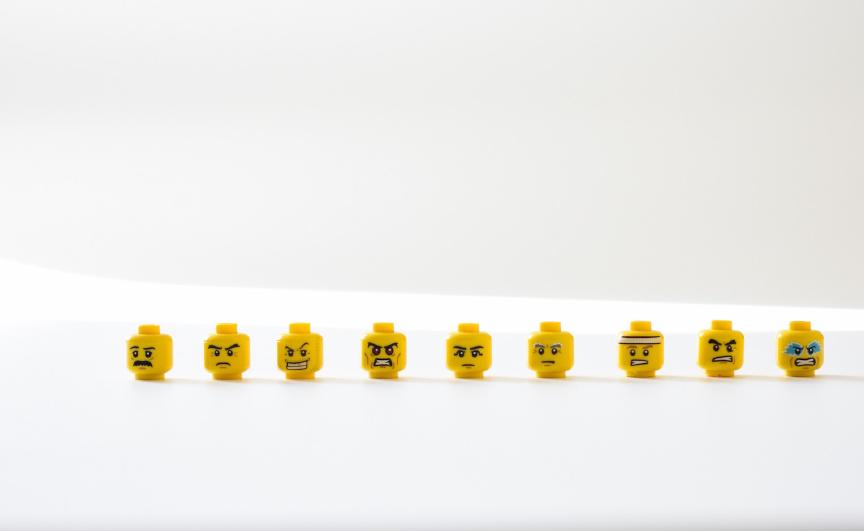
In the vast expanse of digital content, opinions are expressed in various forms and on countless topics. Understanding these sentiments can be invaluable for businesses, researchers, and policymakers alike for market research, product improvement and much more.
This is where Opinion Mining, also known as sentiment analysis, comes into play. Opinion Mining is a powerful technique that involves extracting and interpreting emotions, sentiments, and opinions from the text - something that's not in short supply in this digital world.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Opinion Mining, exploring its significance, techniques, applications, challenges, and prospects.
Opinion mining vs sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis and opinion mining are often used interchangeably, involving natural language processing and text analysis techniques to extract subjective information from various sources.
Sentiment analysis primarily determines whether a piece of writing expresses positivity, negativity, or neutrality. It is commonly employed to gauge public opinion on specific topics, products, or events.
In contrast, opinion mining encompasses various techniques, including sentiment analysis. It goes beyond merely discerning the overall sentiment and delves into extracting specific opinions or emotions from the text. Opinion mining is a comprehensive concept that incorporates sentiment analysis as a subset.
Types of Sentiment
Before we explore the intricacies of Opinion Mining, it is essential to understand the different types of sentiments that can be expressed in text. Sentiment classification can generally be broken down into three categories:
Positive Sentiment:
This type of sentiment reflects satisfaction, happiness, or approval. Positive sentiments are often associated with favourable experiences and play a significant role in shaping attitudes and behaviours. Brands look for positive sentiment toward their product, service or image as a sign that the consumer is happy and satisfied.
Negative Sentiment
Conversely, negative sentiments indicate dissatisfaction, sadness, or disapproval. Negative opinions can arise due to various factors, and understanding them is vital for addressing concerns and improving products or services. It's important to remember that one negative review isn't an indicator of negative sentiment.
Neutral Sentiment
Not all statements express strong emotions. Neutral sentiments are often seen in factual descriptions or objective statements that do not convey a particular sentiment. Neutral sentiment is not a 3/5 star rating or people seeing an experience as 'ok'. Neutral sentiment has no opinion.
Tools for Opinion Mining
Opinion Mining relies on advanced tools and techniques to analyse and interpret sentiments in text.
Some of the key methods include:
Sentiment Analysis Algorithms
Sentiment analysis algorithms use machine learning techniques to classify text into sentiment categories. Support Vector Machines (SVM) and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) are commonly used algorithms within a piece of software that will start mining text on social media platforms and other publications as a way to extract sentiment toward something.
Machine Learning Models
Machine learning models are invaluable tools and techniques for opinion mining. These models play a crucial role in training sentiment analysis systems to automatically identify and categorise sentiments expressed in text data.
To perform sentiment analysis, machine learning models are trained using labelled data, where each piece of text is associated with its corresponding sentiment (e.g., positive, negative, neutral). The models learn from this data and recognise patterns and linguistic cues indicative of different sentiments. This training process enables the models to generalise their understanding of sentiments and apply it to new, unseen text.
Lexicon-Based Approaches
At the core of sentiment, lexicons are meticulously curated repositories that associate words with specific emotions and sentiments. These lexical resources serve as an invaluable reference, allowing the mapping of words to their corresponding sentiments with utmost accuracy.
The strength of lexicon-based approaches lies in their ability to leverage extensive knowledge about emotional language, facilitating nuanced sentiment analysis. By recognising words and phrases that evoke positive, negative, or neutral emotions, these approaches can effectively gauge the overall sentiment expressed in a given piece of text.
Moreover, lexicon-based methods are particularly valuable in scenarios where data for machine learning and AI is scarce or difficult to obtain. They offer a reliable alternative, delivering insightful sentiment analysis without extensive training requirements.
Subjectivity detection
Subjectivity detection is a pivotal qualifier for text to be mined for opinions.
This powerful technique discerns whether a piece of text expresses subjective viewpoints or objective facts. Opinion mining can efficiently extract sentiments, emotions, and attitudes individuals or communities share by focusing solely on subjective content.
On the other side of the coin, subjectivity detection can be used, for example, to identify if a journalistic piece leans more on one side than the other on a political compass. Many digital products have appeared in the last several years that show users news that aligns with their progressive or conservative values and are based on subjectivity detection.
Many of the opinion mining or sentiment analysis techniques listed above are used together as part of a wider system for opinion and text mining.
Opinion Mining Use Cases
Opinion and data mining has found diverse applications across various domains. Some notable applications and techniques using opinion mining:
Social Media Monitoring: Opinion mining facilitates the extraction of explicit and implicit sentiments from the massive pool of social media data, empowering businesses to gauge customer feedback and assess brand reputation in real time. \In the digital age, social media platforms have become a treasure trove of public opinion, offering a vast and dynamic landscape for businesses to explore. Through the powerful process of opinion mining and sentiment analysis on Twitter and other social media data, companies can delve into the sentiments expressed by their customers and the wider online community. Social media mining and social network analysis open doors to understanding public perceptions, preferences, and concerns with unparalleled depth and speed.
Twitter sentiment analysis has emerged as a particularly powerful tool for businesses to gain actionable insights. The analysis of Twitter data provides a window into public sentiment on diverse topics, enabling organisations to stay attuned to the pulse of their audience.
Brand Reputation Management: Safeguarding a positive brand image is paramount for any company. In this pursuit, opinion mining emerges as an indispensable tool, enabling businesses to meticulously monitor sentiments revolving around their brand and make data-driven decisions to uphold their reputation.
By continuously monitoring the current opinion landscape through sentiment analysis, businesses can proactively respond to emerging trends, identify areas for improvement, and capitalise on positive sentiments. Understanding the pulse of public opinion empowers companies to tailor their strategies, refine their products or services, and enhance customer experiences, fostering stronger brand loyalty.
Market Research and Customer Feedback
Opinion Mining has proven invaluable in market research and customer feedback analysis, revolutionising how businesses gather and interpret consumer sentiments. By leveraging opinion mining techniques and methods for sentiment analysis, companies can swiftly delve into the vast sea of data to extract invaluable insights from opinion sentences.
The use of opinion mining in market research allows for real-time data analysis, enabling businesses to stay agile and responsive to emerging trends. By analysing the opinion polarity, businesses can gauge whether sentiments convey positive or negative feedback, providing a comprehensive understanding of customer preferences and satisfaction levels. Opinion mining plays a pivotal role in deciphering customer feedback, uncovering nuanced sentiments, and identifying pain points.
The field of opinion mining has elevated market research to new heights, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions that fuel growth and success. Opinion mining is not just a passing trend; it has become indispensable for any company seeking a competitive edge in today's market.
Ecommerce Cross-selling & Up-selling
In the world of e-commerce, opinion mining stands as a transformative force, reshaping cross-selling and up-selling strategies and elevating companies to new heights of sales and customer experience excellence. By harnessing the power of sentiment analysis and customer feedback, opinion mining unlocks invaluable insights into customer preferences, fueling the creation of personalised recommendations and precisely targeted marketing campaigns.
Amazon, a trailblazer in the e-commerce realm, epitomises the art of leveraging opinion mining for potent cross-selling and up-selling initiatives. Propelled by sophisticated algorithms rooted in deep learning and machine learning techniques, the platform analyses customer reviews, product ratings, and browsing behaviour to unravel individual preferences and purchase patterns. Armed with this knowledge, Amazon curates recommendations for complementary or upgraded products, ushering customers into an enriched shopping experience that significantly amplifies the likelihood of additional purchases.
Notably, opinion mining extends beyond facilitating cross-selling endeavours; it seamlessly empowers Amazon to engage in up-selling tactics. By deftly suggesting premium or higher-priced alternatives in alignment with customers' sentiments and preferences, Amazon crafts a shopping journey tailored to each individual's tastes, elevating customer satisfaction and engendering unswerving loyalty.
At the heart of this transformative process lies the art of data processing on a colossal scale. Opinion mining efficiently navigates big data to extract and decipher sentiments or opinions, employing cutting-edge mining methods and opinion-mining techniques for meticulous analysis.
Challenges in Opinion Mining
Opinion Mining, undoubtedly a powerful tool, has its fair share of challenges. Navigating these hurdles is crucial for achieving accurate and meaningful efficacy of the technology.
Some of the key obstacles that opinion mining faces are as follows:
Sarcasm and Irony Detection
"Wow, what an amazing phone. I love how it magically runs out of battery when I need it the most. And the best part? The constant freezing and lagging really add a thrilling element to my day. Who needs a smooth and reliable user experience when you can have an unpredictable roller coaster ride with your phone."
The realm of sentiment analysis grapples with the intricate task of identifying sarcasm and irony in textual data. These forms of expression often convey sentiments opposite to the literal meaning of words, confounding sentiment analysis algorithms. Detecting subtle linguistic and context clues becomes imperative to accurately discern sarcasm and irony, ensuring a faithful representation of sentiment.
Multilingual Sentiment Analysis
In our diverse global landscape, sentiment analysis extends beyond a single language. Different languages and cultural nuances introduce additional layers of complexity. Language-specific models and datasets become indispensable for capturing the intricacies of sentiment across diverse linguistic contexts.
Let's look at an example:
In Spanish, "simpático" is often used to describe someone friendly, pleasant, and likeable. However, in some contexts, it can also carry the connotation of being overly agreeable or irritating, which may be viewed as a negative trait in, for example, shop assistants.
Achieving cross-lingual sentiment analysis proficiency requires specialised techniques addressing the challenge of language variation.
Context Understanding
Context plays a pivotal role in determining the emotional connotation of words. Words may carry distinct emotions depending on the context in which they are used. This necessitates a sophisticated understanding of contextual nuances to avoid misinterpretations in sentiment analysis.
For example, Karen's Diner, a restaurant that bases its experience around the rude wait staff, has many negative reviews - but that's precisely the premise of the place.
Algorithms must be equipped to discern the underlying context and adapt their analysis accordingly to deliver accurate insights.
Subjectivity and Ambiguity
The subjectivity and ambiguity inherent in human language present another challenge for opinion mining to analyse sentiments. Human expressions are not always easily classified into predefined sentiment categories. As such, sentiment analysis models must be adaptive and versatile, capable of capturing a broader range of emotional expressions and handling ambiguous sentiments adeptly.
Emotional Intensity
Sentiments are not homogenous; they vary in intensity, from subtle emotions to intense feelings. Accurately gauging emotional intensity in text enhances the depth of sentiment analysis. Advanced opinion mining techniques must be able to assess the strength of emotions, ensuring a nuanced understanding of sentiment expression.
Ethical Considerations in Opinion Mining
Like any technology, Opinion Mining presents a range of ethical concerns that demand careful attention and resolution. These concerns encompass various aspects of the technology's deployment, from privacy considerations to potential bias and misuse. Addressing these ethical implications is imperative to ensure that Opinion Mining is employed responsibly and beneficially.
Privacy Concerns
One of the most pressing ethical dilemmas in Opinion Mining revolves around privacy. Extracting opinions from public platforms may inadvertently intrude upon individuals' privacy rights. Without explicit consent or knowledge, mining individual opinions raises red flags about the ethical handling of personal data. To safeguard user privacy, developers must implement stringent measures to obtain consent and anonymise data whenever possible. Transparency regarding data collection and usage practices is essential to foster trust among users and protect their right to privacy.
Bias and Fairness Issues
The potential for bias in sentiment analysis is a critical ethical consideration in Opinion Mining. Biased sentiment analysis algorithms may perpetuate stereotypes, leading to unfair judgments and decisions. Such biases can be rooted in the data used for training the algorithms, reflecting societal prejudices and imbalances. To mitigate bias, developers should employ diverse and representative training datasets, actively identifying and eliminating potential sources of bias. Investing in ongoing research to enhance algorithmic fairness can help ensure unbiased sentiment analysis, ultimately promoting more equitable outcomes.
Misuse of Opinion mining
A profound ethical responsibility lies with practitioners and organisations utilising Opinion Mining to deploy the technology responsibly. Misusing sentiment analysis can have far-reaching consequences, such as manipulating public opinion or disseminating misinformation.
One such example is 'astroturfing' during a political campaign: It refers to a deceptive and manipulative practice where political actors create fake social media accounts further to promote fabricated positive sentiments about their candidate. This orchestrated show of support is designed to sway undecided voters and create a false impression of grassroots backing.
Clear guidelines and ethical frameworks must be established to counteract such risks to govern the use of Opinion Mining tools. Encouraging transparency and accountability in data collection, analysis, and reporting practices can prevent the manipulation of sentiments and safeguard the integrity of public discourse.
Future Trends in Opinion Mining & Text Analysis
The horizon of Opinion Mining is brimming with potential, poised to revolutionise how we perceive and interpret public sentiment. Several promising advancements are on the horizon, driven by ongoing developments in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and the growing integration of AI systems.
Real-Time Opinion Tracking
The future of Opinion Mining will empower businesses, policymakers, and organisations with real-time sentiment-tracking capabilities. Rapid advancements in data processing and cloud computing will enable sentiment analysis systems to analyse vast data streams from social media, news outlets, and other online platforms in real time. This real-time analysis will provide invaluable insights into emerging trends, public reactions to events, and evolving sentiments, allowing for swift and informed decision-making.
Integration with AI Systems
Opinion Mining will increasingly intersect with various AI systems, amplifying their utility and impact. Sentiment analysis will become integral to AI-driven decision-making processes, enabling businesses to gauge consumer satisfaction, identify potential risks, and tailor their offerings according to prevailing sentiments. In customer service, AI chatbots equipped with sentiment analysis capabilities will respond empathetically and effectively to customers' emotional states, enhancing user experiences.
Multimodal Sentiment Analysis
The future will witness a shift toward multimodal sentiment analysis, where systems will rely on text data and process visual and auditory cues to understand the sentiment. Integrating data from images, videos, and audio recordings with textual information will provide a more comprehensive and accurate sentiment assessment, catering to the diverse ways people express their emotions online.
Ethical AI and Bias Mitigation
In tandem with advancements in Opinion Mining, ethical considerations will take centre stage. Developers will prioritise fairness, transparency, and accountability in sentiment analysis systems, addressing biases arising from training data and algorithms. Efforts will be made to ensure that sentiment analysis benefits all users without reinforcing societal prejudices or causing harm.
Cross-Lingual Sentiment Analysis
Cross-lingual sentiment analysis will become crucial with the increasing globalisation of businesses and online interactions. Advancements in multilingual NLP models and translation techniques will enable sentiment analysis systems to understand opinions expressed in different languages, fostering greater inclusivity and accessibility in understanding global sentiments.
Conclusion
As we navigate the dynamic landscape of sentiment analysis, it is clear that Opinion Mining will continue to be a pivotal tool in extracting valuable sentiments from the vast ocean of digital content. Its impact will extend beyond market research, brand reputation management, and social media monitoring to shape how businesses and organisations understand and respond to public sentiments.
By embracing ethical principles and the future trends in Opinion Mining, we can harness its transformative power to navigate the complexities of human emotions and opinions in the digital age.
Get a glimpse into the future of business communication with digital natives.
Get the FREE report